|
Monday started off with an unalarming 0.2 percent rise for the core PCE price index and was followed on Tuesday by an even more unalarming 2 tenths drop in consumer inflation expectations. It was Wednesday when the trouble started. The morning's rise in the employment cost index didn't seem to register but what did was Wednesday afternoon's FOMC statement where inflation expectations got an upgrade. Then on Friday, average hourly earnings popped higher to spark, perhaps for the first time in our post-2008 expansion, serious talk about wage inflation, a risk the Fed traditionally heads off at the expense of the stock market. But of course there's always two sides to every story and certainly two sides to nearly every economic report, as we shall see.
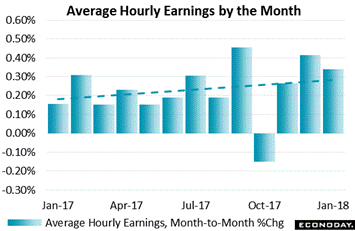 Average hourly earnings rose 0.3 percent in January which was actually Econoday's consensus forecast. What wasn't forecast was a 1 tenth upward revision to 0.4 percent for December, one as traced in the graph that heightens a rising trendline. And when going out 2 decimal places, December is yet a little higher, at 0.41 percent, and January, at 0.34 percent, is nearly rounded up. These of course are nuances but attention to detail, like that in the FOMC statement, can't hurt when looking for pivot points. Average hourly earnings rose 0.3 percent in January which was actually Econoday's consensus forecast. What wasn't forecast was a 1 tenth upward revision to 0.4 percent for December, one as traced in the graph that heightens a rising trendline. And when going out 2 decimal places, December is yet a little higher, at 0.41 percent, and January, at 0.34 percent, is nearly rounded up. These of course are nuances but attention to detail, like that in the FOMC statement, can't hurt when looking for pivot points.
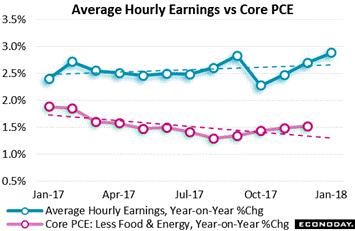 The shift in January's FOMC statement is the nailing down of a calendar target for inflation, that year-on-year inflation will move higher "this year" and stabilize "around" the Fed's 2 percent objective. The FOMC's prior assessments of inflation were more flat than up, not clearly moving higher. Turning back to average hourly earnings, the biggest headline wasn't the monthly rate but year-on-year growth which jumped to an expansion best of 2.9 percent. This is now near the 3 percent line over which wage pressures, at least policy hawks argue, begin to feed into overall inflation. The core PCE rate, the Fed's central inflation measure, actually didn't make any news in Monday's personal income & outlays report, posting only a 0.2 percent December gain and no improvement for the yearly rate which is stuck at the 1.5 percent line. Yet if wages keep increasing, spillover could begin to lift the red line higher, perhaps as early as January's PCE report later this month. The shift in January's FOMC statement is the nailing down of a calendar target for inflation, that year-on-year inflation will move higher "this year" and stabilize "around" the Fed's 2 percent objective. The FOMC's prior assessments of inflation were more flat than up, not clearly moving higher. Turning back to average hourly earnings, the biggest headline wasn't the monthly rate but year-on-year growth which jumped to an expansion best of 2.9 percent. This is now near the 3 percent line over which wage pressures, at least policy hawks argue, begin to feed into overall inflation. The core PCE rate, the Fed's central inflation measure, actually didn't make any news in Monday's personal income & outlays report, posting only a 0.2 percent December gain and no improvement for the yearly rate which is stuck at the 1.5 percent line. Yet if wages keep increasing, spillover could begin to lift the red line higher, perhaps as early as January's PCE report later this month.
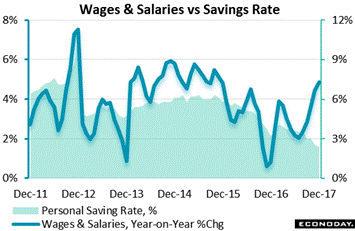 But there was a highlight in Monday's personal income report and that is the wages & salaries component which extended its string of 0.4 and 0.5 percent monthly gains. The year-on-year rate, tracked in the blue line, rose to 4.9 percent for its 5th straight climb and now at its highest rate since November 2015. But now the twists start. The gains for wages aren't helping the saving rate, at least not yet. The savings rate, at 2.4 percent as tracked in the green background, is the lowest in 13 years and helps explain, together perhaps with rising wages but also with rising credit-card debt, the solid strength of the holiday shopping season. But there was a highlight in Monday's personal income report and that is the wages & salaries component which extended its string of 0.4 and 0.5 percent monthly gains. The year-on-year rate, tracked in the blue line, rose to 4.9 percent for its 5th straight climb and now at its highest rate since November 2015. But now the twists start. The gains for wages aren't helping the saving rate, at least not yet. The savings rate, at 2.4 percent as tracked in the green background, is the lowest in 13 years and helps explain, together perhaps with rising wages but also with rising credit-card debt, the solid strength of the holiday shopping season.
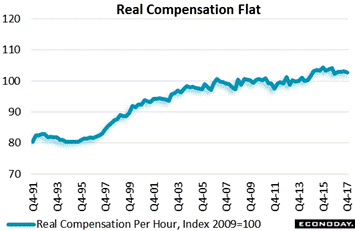 Not all the data are pointing to a pivot higher for wages. Real compensation, that is inflation-adjusted compensation released with the week's fourth-quarter productivity report, proved flat once again as tracked in the blue line which has been unable to move much above the 100 line, where the index was set way back in 2009. For 2017 as a whole, real compensation fell 0.6 percent for the deepest decline since 2011. Real compensation also fell in 2016, down 0.2 percent which makes this the first back-to-back negative years since 1993 and 1994. If wage-push inflation does begin to kick in, the gains will have to exceed the rate of consumer inflation otherwise real compensation won't be going anywhere. Not all the data are pointing to a pivot higher for wages. Real compensation, that is inflation-adjusted compensation released with the week's fourth-quarter productivity report, proved flat once again as tracked in the blue line which has been unable to move much above the 100 line, where the index was set way back in 2009. For 2017 as a whole, real compensation fell 0.6 percent for the deepest decline since 2011. Real compensation also fell in 2016, down 0.2 percent which makes this the first back-to-back negative years since 1993 and 1994. If wage-push inflation does begin to kick in, the gains will have to exceed the rate of consumer inflation otherwise real compensation won't be going anywhere.
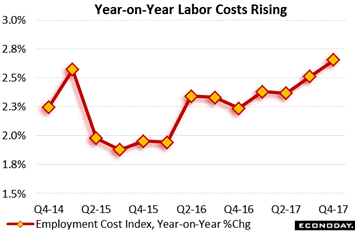 Yet another inflation gauge was released in the week, one that is a favorite at the Fed. The employment cost index tracks the mirror image of wages, that is employer costs, measured here both in terms of wages & salaries and also benefits, both of which have posting comparable and moderate increases. The composite index, tracked by the red line, rose 1 tenth in the fourth quarter to 2.66 percent which for this closely watched reading is the highest since 2008. For employers and inflation hawks, the level is manageable but the direction is unmistakable and fits with Fed expectations for a visible rise in inflation. Yet another inflation gauge was released in the week, one that is a favorite at the Fed. The employment cost index tracks the mirror image of wages, that is employer costs, measured here both in terms of wages & salaries and also benefits, both of which have posting comparable and moderate increases. The composite index, tracked by the red line, rose 1 tenth in the fourth quarter to 2.66 percent which for this closely watched reading is the highest since 2008. For employers and inflation hawks, the level is manageable but the direction is unmistakable and fits with Fed expectations for a visible rise in inflation.
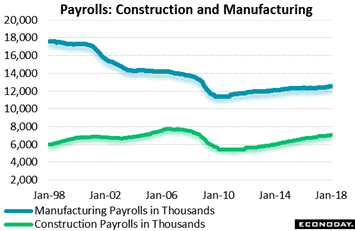 And employers may continue to pay higher costs given the scarcity of available labor. Payroll data have been proving very healthy and are being led by two key sectors, manufacturing and construction. Manufacturing payrolls have been rising at 20,000 per month clips the past 6 months which is their best showing since before the 2014 oil collapse. Construction, where total payrolls are much lower, has been averaging nearly 28,000 gains the past 6 months which fits in with the rising strength underway in the housing sector. Note in the graph that construction payrolls will soon be approaching the nearly 8 million peak of the prior expansion, yet for manufacturing where, unlike construction, production doesn't have to be onshore, prior levels look impossible to regain. This is evidence enough of 20 years of offshoring. And employers may continue to pay higher costs given the scarcity of available labor. Payroll data have been proving very healthy and are being led by two key sectors, manufacturing and construction. Manufacturing payrolls have been rising at 20,000 per month clips the past 6 months which is their best showing since before the 2014 oil collapse. Construction, where total payrolls are much lower, has been averaging nearly 28,000 gains the past 6 months which fits in with the rising strength underway in the housing sector. Note in the graph that construction payrolls will soon be approaching the nearly 8 million peak of the prior expansion, yet for manufacturing where, unlike construction, production doesn't have to be onshore, prior levels look impossible to regain. This is evidence enough of 20 years of offshoring.
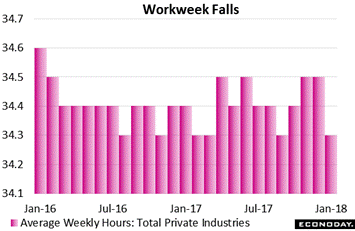 There was an unexpected and counter intuitive weakness in the January employment report. Despite strong general strength, the workweek fell sharply to 34.3 hours vs 34.5 hours in the prior two months. A topping off in hours is not consistent with wage pressures nor an overheating labor market. Could the decline be tied to the month's government shutdown, however brief it was? The Labor Department doesn't think so, saying the shutdown had "no discernable effect" on the report. Declining hours certainly couldn't reflect a lack of work given strong sales at the retail level, unusually heavy sales at the wholesale level, nor factory orders which have been rising. But maybe they could be a symptom of the labor market itself, what the Fed's Beige Book has been warning: that lack of available workers is holding down the expansion, that businesses can't find the people they need to keep production where they want it. There was an unexpected and counter intuitive weakness in the January employment report. Despite strong general strength, the workweek fell sharply to 34.3 hours vs 34.5 hours in the prior two months. A topping off in hours is not consistent with wage pressures nor an overheating labor market. Could the decline be tied to the month's government shutdown, however brief it was? The Labor Department doesn't think so, saying the shutdown had "no discernable effect" on the report. Declining hours certainly couldn't reflect a lack of work given strong sales at the retail level, unusually heavy sales at the wholesale level, nor factory orders which have been rising. But maybe they could be a symptom of the labor market itself, what the Fed's Beige Book has been warning: that lack of available workers is holding down the expansion, that businesses can't find the people they need to keep production where they want it.
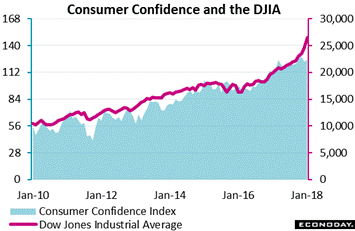 We started off the week's rundown mentioning inflation expectations which, in another contradiction of wage gains, continue to show no life at all, down 2 tenths in the Conference Board's consumer confidence report to 4.6 percent which for this specific reading is very low. Yet the index for confidence, underpinned by very strong assessments of the labor market, is holding at 17-year highs, at 125.4 in January. But it may not be wages that consumers are confident about but the stock market instead where those seeing future gains spiked more than 5 percentage points to 51.6 percent, dwarfing those seeing a decline which fell to 19.9 percent. If this isn't good news for market contrarians, what is? The graph tracks consumer confidence against the Dow; their mutual ascent speaks for itself. We started off the week's rundown mentioning inflation expectations which, in another contradiction of wage gains, continue to show no life at all, down 2 tenths in the Conference Board's consumer confidence report to 4.6 percent which for this specific reading is very low. Yet the index for confidence, underpinned by very strong assessments of the labor market, is holding at 17-year highs, at 125.4 in January. But it may not be wages that consumers are confident about but the stock market instead where those seeing future gains spiked more than 5 percentage points to 51.6 percent, dwarfing those seeing a decline which fell to 19.9 percent. If this isn't good news for market contrarians, what is? The graph tracks consumer confidence against the Dow; their mutual ascent speaks for itself.
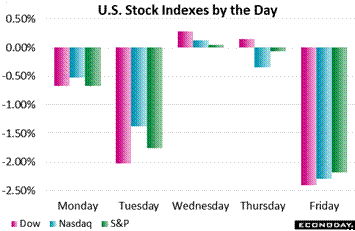 As the inflation scare set in, stocks moved sharply lower. The Dow lost 4.1 percent on the week to trim its year-to-date gain in this still very young year to a still strong 3.2 percent. Falling demand for bonds was another of the week's stories. The 10-year shot 18 basis points higher in heavy selling to 2.84 percent, a rate that is 18 basis points higher in the week and an attractive 43 points higher than year-end. Though general economic strength and possible inflation spell less accommodation and less bond buying from global central banks, investor desire for a high rate of safe yield may be a limiting factor in any future bond selloffs. As the inflation scare set in, stocks moved sharply lower. The Dow lost 4.1 percent on the week to trim its year-to-date gain in this still very young year to a still strong 3.2 percent. Falling demand for bonds was another of the week's stories. The 10-year shot 18 basis points higher in heavy selling to 2.84 percent, a rate that is 18 basis points higher in the week and an attractive 43 points higher than year-end. Though general economic strength and possible inflation spell less accommodation and less bond buying from global central banks, investor desire for a high rate of safe yield may be a limiting factor in any future bond selloffs.
| Markets at a Glance |
Year-End |
Week Ended |
Week Ended |
Year-To-Date |
Weekly |
|
2017 |
26-Jan-18 |
2-Feb-18 |
Change |
Change |
| DJIA |
24,719.22 |
26,616.71 |
25,520.96 |
3.2% |
-4.1% |
| S&P 500 |
2,673.61 |
2,872.87 |
2,762.13 |
3.3% |
-3.9% |
| Nasdaq Composite |
6,903.39 |
7,505.77 |
7,240.95 |
4.9% |
-3.5% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Crude Oil, WTI ($/barrel) |
$60.15 |
$66.14 |
$65.13 |
8.3% |
-1.5% |
| Gold (COMEX) ($/ounce) |
$1,305.50 |
$1,354.20 |
$1,332.70 |
2.1% |
-1.6% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fed Funds Target |
1.25 to 1.50% |
1.25 to 1.50% |
1.25 to 1.50% |
0 bp |
0 bp |
| 2-Year Treasury Yield |
1.89% |
2.11% |
2.14% |
25 bp |
3 bp |
| 10-Year Treasury Yield |
2.41% |
2.66% |
2.84% |
43 bp |
18 bp |
| Dollar Index |
92.29 |
89.12 |
89.16 |
-3.4% |
0.0% |
The jury is still out if wages are in fact pivoting higher but the question is now definitely on the table. Average hourly earnings are only one reading and though others are also showing pressure, real compensation remains flat. Yet the data in sum do justify the FOMC's inflation upgrade, however modest and gradual any improvement may prove.
After two weeks of an unusually heavy release schedule, the coming week's slate is light and led off on Monday by two indications on the service sector, Markit and ISM, both of which have been showing easing strength. Tuesday is the heaviest day of the week, opening with the monthly trade report, where a deepening deficit is the call, and including JOLTS data and the latest on job openings which have been slowing. Wednesday's highlight will be consumer credit which will update credit-card use followed on Thursday with jobless claims, which may have now stabilized, and on Friday by wholesale trade where the need to build inventories is a hidden plus for the first quarter.
PMI Services for January, Final
Consensus Forecast: 53.3
Consensus Range: 53.3 to 53.5
PMI services proved soft at the headline level, held down by soft output and coming in under expectations at 53.3 for the January flash. Yet details were solid including acceleration for both new orders and employment and also traction for selling prices. Econoday's consensus for the January final is the same as the flash, at 53.3.
ISM Non-Manufacturing Index for January
Consensus Forecast: 56.2
Consensus Range: 55.2 to 57.0
The ISM non-manufacturing index has been cooling noticeably, moving down from the 60 area in October to what was a lower-than-expected 56.0 in December (revised from an initial 55.9). But most readings were still in the mid-50s to indicate solid monthly growth including new orders at 54.2, new export orders at 56.5, and employment at 56.3. Forecasters are calling for 56.2 in January.
International Trade Balance for December
Consensus Forecast: -$51.9 billion
Consensus Range: -$52.5 billion to -$51.2 billion
The international trade deficit is expected to widen sharply in December to $51.9 billion from November's already steep deficit of $50.5 billion. Advance data on the goods portion of this report showed widening in December as a rise in imports offset and overshadowed what was a very good showing for exports.
JOLTS: Job Openings for December
Consensus Forecast: 5.900 million
Consensus Range: 5.900 to 5.980 million
Job openings are high but did slip 0.8 percent to 5.879 million in the last JOLTS report for November. Hires also fell, down 1.9 percent to 5.488 million. Openings have been moving lower after peaking at 6.140 million in July, while hires, despite November's dip, have been picking up and are still near their expansion high which was set in October at 5.592 million. Econoday's consensus for December job openings is for a slight gain to 5.900 million.
Consumer Credit for December
Consensus Forecast: $20.0 billion
Consensus Range: $17.9 billion to $22.0 billion
Consumers are not only been dipping into their savings, they've also been drawing on their credit cards to an increasing degree as revolving credit rose $11.2 billion in November and made a sizable contribution to total credit outstanding which climbed $28 billion for a 17-year high. November's rise in revolving credit was the second largest of the post-2008 expansion and hints at less reluctance among consumers to run up credit-card debt. December's total consumer credit outstanding is expected to rise $20.0 billion.
Initial Jobless Claims for February 3 week
Consensus Forecast: 235,000
Consensus Range: 232,000 to 235,000
After a long spell of volatility, initial claims are expected to come in at 235,000 in the February 3 week in what, after 230,000 and 231,000 in the prior two weeks, would extend the lowest and most stable run since August. Volatile or not, jobless claims have been very low in confirmation that labor demand is strong.
Wholesale Inventories for December
Consensus Forecast, Month-to-Month Change: 0.2%
Consensus Range: -0.4% to 0.2%
December wholesale trade inventories are expected to rise 0.2 percent in line with advance data which also showed a 0.2 percent build. Inventory build -- due to strong demand -- slowed in the fourth quarter in what held down GDP, yet this points to the need for restocking in the first quarter and gains in turn for production and employment.
|

